In the middle of July 2021, a large forest fire broke out in northern California. Known under the name of “Dixie”, it became the second-largest wildfire in the state’s history. The blaze got its name after Dixie Road, near which the fire began in Butte County.
The fire’s unofficial name was “Monster” – exactly with this word many newspapers and online resources referred to this natural disaster. The Dixie Fire affected five counties in the state - Butte, Lassen, Plumas, Shasta, and Tehama.
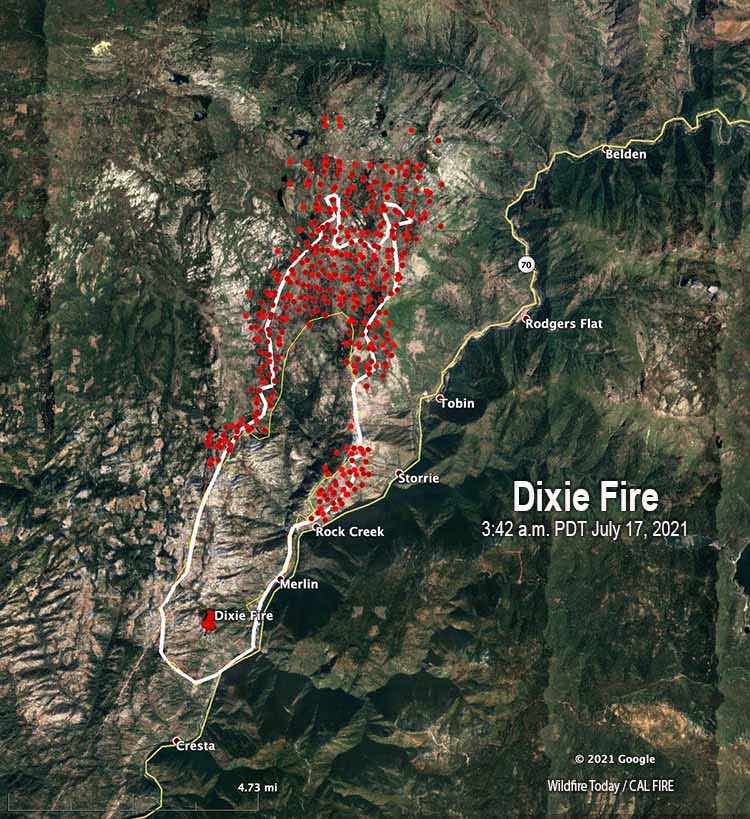
Image source: Wildfire Today
According to statistics, California is the most wildfire-prone state in the U.S., mostly due to natural factors. Because of its Mediterranean climate, the state is dry most of the year, with rains falling only in winter, which is followed by dry and hot summers.
Plants growing in this region consist of dry grass, shrubs, and pine needles, which are very easy to ignite. Combined with the dry weather, this vegetation acts as fuel for a fire. Additionally, climate change contributed to the fact that the land and plants become even drier than usual and thus more favorable for a fire to spread.
| Rank | State | Number of fires |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | California | 9,260 |
| 2 | Texas | 5,576 |
| 3 | North Carolina | 5,151 |
| 4 | Montana | 2,573 |
| 5 | Florida | 2,262 |
| 6 | Oregon | 2,202 |
| 7 | Georgia | 2,139 |
| 8 | Minnesota | 2,065 |
| 9 | Washington | 1,863 |
| 10 | Arizona | 1,773 |
Table source: Insurance Information Institute
In recent years, wildfires have become more intense. For example, over the past two years, they scorched an area larger than the total area of New Jersey and Vermont.
The Dixie Fire covered almost 1 million acres in California. Having analyzed Dixie’s growth trajectory, researchers came to the conclusion that the largest growth spikes occurred on days with high temperatures, low humidity, and high winds.
The firefighting efforts cost $ 637 million and lasted nearly two months, making Dixie the most extensive and expensive fire in California history. According to the research team, the fire’s history determined much of its severity. Additionally, low-intensity firefighting activities had the most significant impact on the elimination of the fire’s worst effects.
Dixie Fire Timeline
Like many other recent environmental disasters, the Dixie Fire started with human error. According to a report by Pacific Gas & Electric Co., on July 13, 2021, a worker in the Feather River Canyon area found two blown fuses and a large tree leaning against a power line wire. A fire was burning at the tree’s bottom.
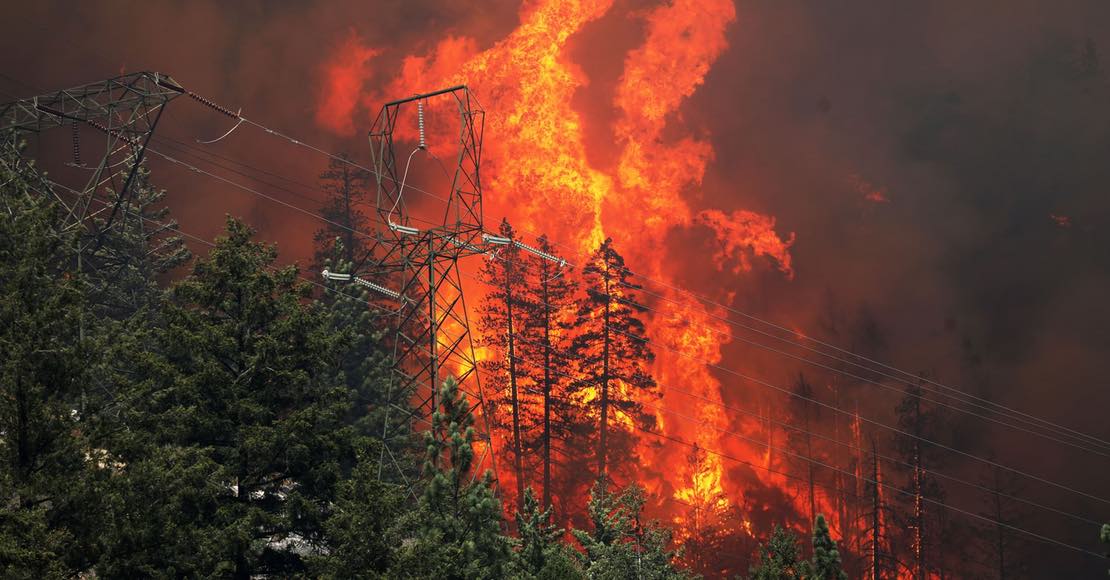

Image source: The Atlantic
The next day, the fire grew to 500 acres. Wind gusts and low humidity contributed to its growth. By the end of the day, the fire was raging already on 2,200 acres of land and was not going to stop. After that, the Dixie Fire headed along the Feather River Canyon to the western shore of Lake Almanor.
Dry grass made it easy for the fire to spread even faster. Additionally, the fire was so violent that it created its own giant cloud, which could generate lightning bolts and thus produce more fires. Such clouds typically appear during volcanic eruptions.
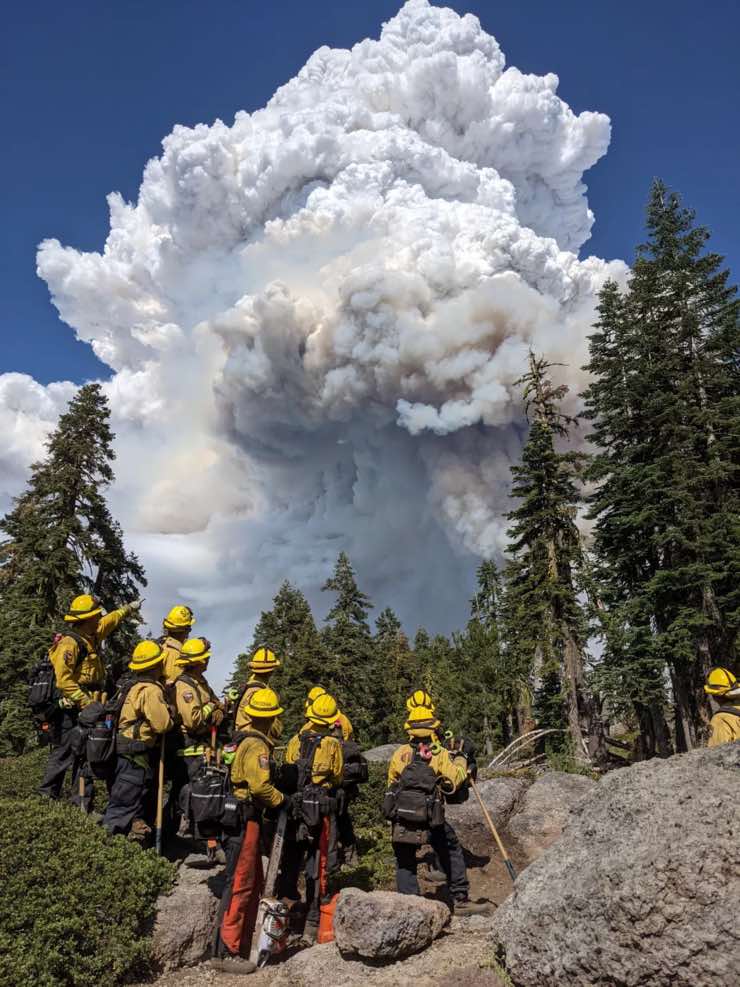

Image source: LA Times
The rocky terrain on Dixie’s way hampered the work of fire crews and thus created favorable conditions for the fire to spread. Canyons, valleys, and peaks acted like chimneys. As of July 21, the fire was put down by only 15 %.
In late July, the Dixie Fire merged with the smaller Fly Fire. By July 30, Dixie covered 240,595 acres of land and became the 11th most devastating wildfire in the history of the state.
In early August, the Dixie Fire split into two parts, one on the western shore of Lake Almanor and another one in the direction of Indian Valley. On August 3, strong winds gave the fire more strength, so it headed to the Lassen Volcanic National Park.
The next day, the Dixie Fire almost completely destroyed the town of Greenville with historic wooden buildings.
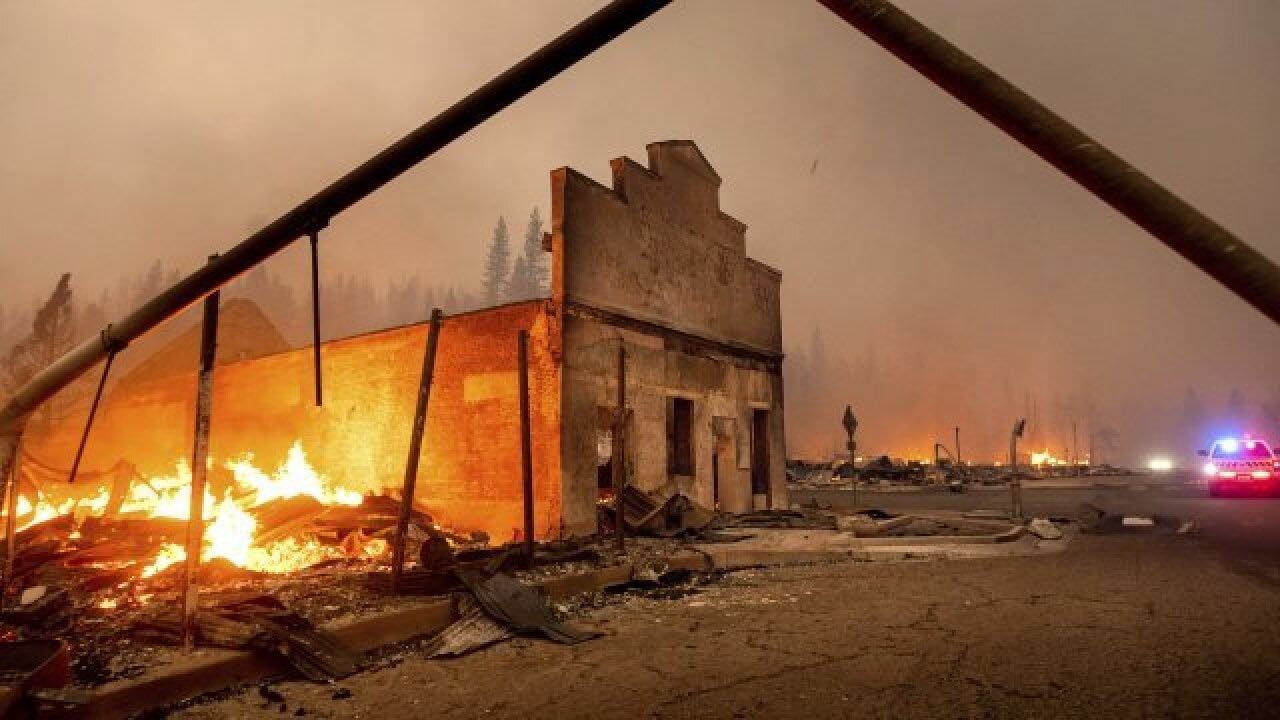

Image source: Fox13
As of August 4, the blaze covered 320,000 acres and was extinguished by 35 %. It also rose in its ranking from the 11th to the 6th place among the California wildfires. However, just in 4 days, it became the second-largest fire, having grown to 463,477 acres.
On August 18, the Dixie Fire merged with the Morgan Fire. Both of them continued to destroy the Lassen Volcanic National Park and threatened the towns of Mill Creek and Mineral. By the evening, Dixie covered over 635,000 acres of land. By August 22, the fire was extinguished by 37 %.
In the Lassen Volcanic National Park, Dixie Fire destroyed seven cabins within the Drakesbad Guest Ranch - a historic lodging area built in 1900 and renovated in 1938.
As of September, Dixie was raging in two zones – East Zone (Plumas National Forest) and West Zone (Lassen Volcanic National Park and Lassen National Forest). Thanks to more favorable weather conditions, the firefighters managed to put down 86 % of the fire by September 16. On October 1, the fire containment reached 94 %.
Consequences of the Dixie Fire
The Dixie Fire affected almost one million acres of land. In total, this burned area is bigger than Chicago, Dallas, Los Angeles, and New York City together. It took away the life of one firefighter and injured three firefighters, but there were no deaths among civilians.
The blaze destroyed 600 homes. Additionally, the Dixie Fire burned down the towns of Greenville, Canyondam, and Indian Falls almost completely. The town of Chester nearby survived the fire thanks to the less steep terrain and thinner vegetation.
The total number of destroyed structures is about 1,300, according to Cal Fire.
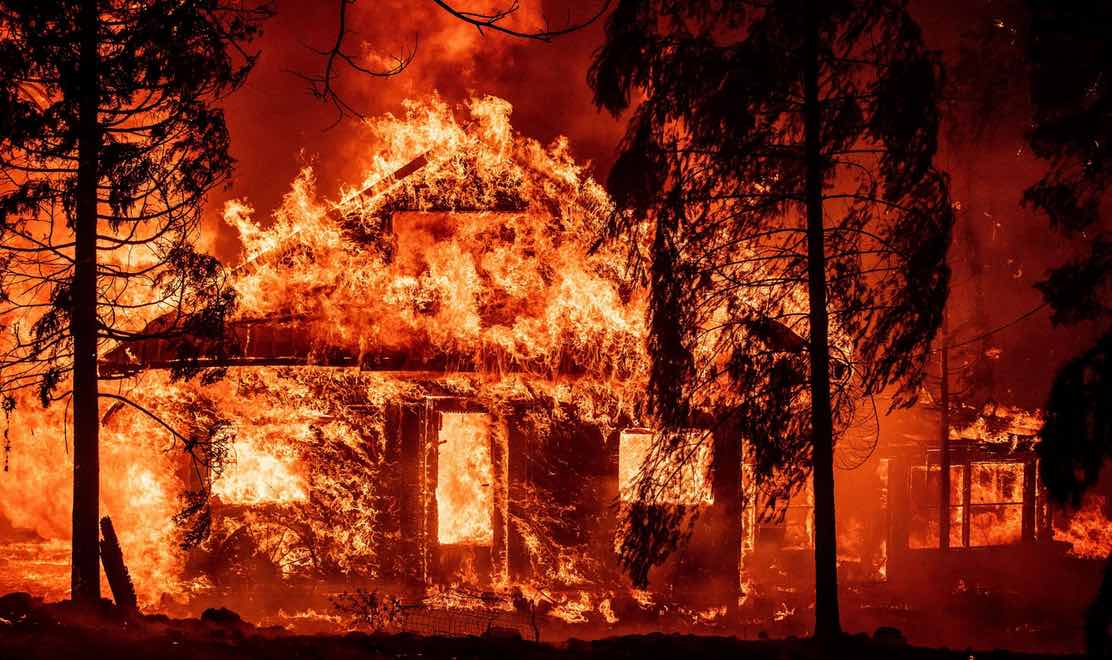

Image source: The Atlantic
Smoke from the Dixie Fire impacted the air quality in the western United States. On August 6, the fine airborne particle levels in Salt Lake City rose more than three times the federal standard.
As a result, the area temporarily topped in the world’s air quality anti-rating. The particles that caused Utah’s poor air quality came from the Dixie Fire and other fires.
The Dixie Fire was the costliest fire in the history of the United States, partly because of hiring highly-paid local and private firefighters. In total, 6,500 persons and hundreds of vehicles were involved in the fire containment activities.
The final cost of extinguishing the Dixie Fire was $ 637.4 million, distributed among several agencies such as the U.S. Forest Service and Cal Fire.
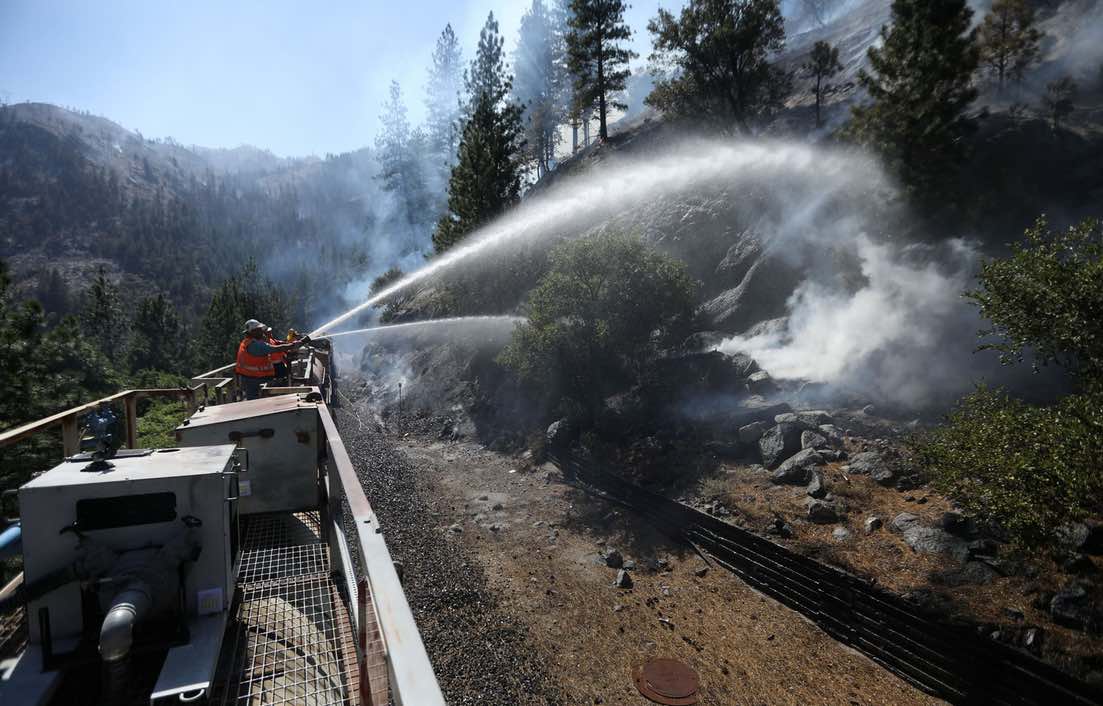

Image source: The Atlantic
PG & E Co. has been scrutinized in recent years because of the role of its equipment in a series of deadly and destructive fires in California, including the Dixie Fire. Specifically, Cal Fire researchers noted that several wildfires have occurred in the same area in recent years, e.g. the deadly Camp Fire of 2018, which also involved PG & E equipment.
After the Dixie Fire, the company announced that it would put 10,000 miles of its power lines underground. According to them, this would help to minimize the risk of further wildfires.
An interesting fact: Timber from trees that Dixie had destroyed was used to build a sawmill in the town of Crescent Mills. This mill would create rough-cut lumber to help rebuild communities that the Dixie Fire burned.
Conclusion
Due to the heat and drought, which are getting worse with climate change, it is becoming increasingly difficult for authorities to fight wildfires in the western United States every season.
According to an August 10 report from the National Interagency Fire Center, there were 108 active large single and “complex” fires in the country that day.
Fires like Dixie are unpredictable, and this makes them dangerous. Throughout a single day, a small fire of just one tree turned into a monster that could even build its own ecosystem.
Therefore, it is important to evacuate beforehand, even before receiving the evacuation warnings from authorities. You can actually get warnings about severe weather conditions directly to your smartphone and thus be prepared to the worst-case scenario.
Here’s how you can activate and receive severe weather alerts for any location in RainViewer:
- On the main screen, tap the Notifications icon.
- Under Custom Notifications, tap the location for which you would like to receive the alerts.
- Turn on Customize Notifications, and then activate Severe Weather Alerts.
As a result, you will start receiving timely notifications about extreme weather conditions, including fires, and see the affected areas on the live map. This will allow you to efficiently plan your evacuation and stay safe.






