Weather radar is more than just a colorful map. It’s a powerful tool for tracking storms, analyzing precipitation, and spotting severe weather before it strikes. But here’s something many don’t realize: not all radar images are created equal. The clarity and accuracy of what you see depend on a crucial factor - radar resolution. Understanding radar resolution can help you make better predictions and avoid misinterpretations. Let’s break it down.
What Is Radar Resolution?
Radar resolution determines how much detail a radar system can capture. Two key factors come into play:
- Spatial resolution. The finer the resolution, the more details the radar can detect. High-resolution radar can distinguish between individual storm cells, while low-resolution radar may blur them together.
- Temporal resolution. This refers to how often the radar updates. Faster updates mean you can track rapid changes in storm intensity and movement with greater precision.
Together, these factors shape how accurately radar reflects real-time weather conditions, making them crucial for meteorologists, storm chasers, and everyday users tracking weather patterns.
Why Spatial Resolution Matters
Think of a high-resolution image versus a pixelated one - the difference is just as dramatic with radar. High spatial resolution can:
- Identify small-scale features like rotating updrafts, an early tornado signal.
- Separate light rain from heavy downpours, improving precipitation estimates.
- Distinguish storm cells, making tracking more precise.

Source: National Weather Service of the United States
The Role of Temporal Resolution
Radar isn’t static; it refreshes at set intervals. The quicker the refresh rate, the better you can track weather shifts in real time. This is crucial for fast-evolving events like:
- Tornado development: Spot rotation before a warning is issued.
- Flash flooding: Identify rapid rainfall increases.
- Thunderstorm intensification: Monitor storm growth minute by minute.
- Sudden wind gusts: Detect short-lived but powerful bursts of wind.
Example
The National Severe Storms Lab demonstrated that a phased-array radar (PAR) could capture 16 images in the time a traditional NEXRAD produced 2 images. Such high temporal resolution significantly improves the accuracy of tornado tracking.
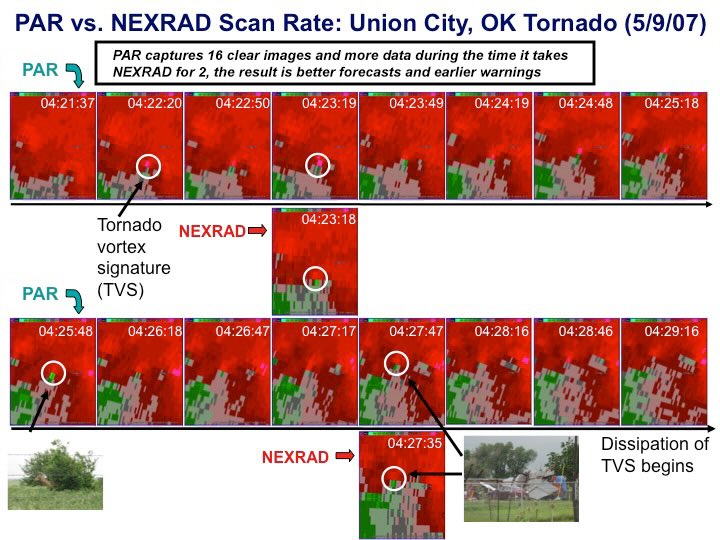
Source: NOAA
What Affects Radar Resolution?
Several factors influence radar resolution, determining how accurately you see storms forming and evolving.
1. Radar Beam Width

Source: Tony Hurt, National Weather Service
The farther a radar beam travels, the wider it spreads, reducing resolution at greater distances. This means:
- Near the radar site: Sharper, more detailed images.
- Farther away: Less clarity, more blending of weather features.
2. Radar Wavelength (Band Type)
Different radar bands offer different trade-offs:
- S-band (long wavelength): Great for long-range scanning but lower resolution.
- C-band: A balance between range and detail.
- X-band (short wavelength): High resolution but limited range.
Meteorologists often use a mix of radar bands to ensure both wide coverage and high detail where needed.
3. Data Processing Techniques
Some radar systems use interpolation to fill in gaps, smoothing the image. While this can make radar maps easier to interpret, it may obscure finer details.
Some radars also use dual-polarization technology, which sends radar beams both horizontally and vertically, improving precipitation type detection (rain, snow, hail) and enhancing resolution.
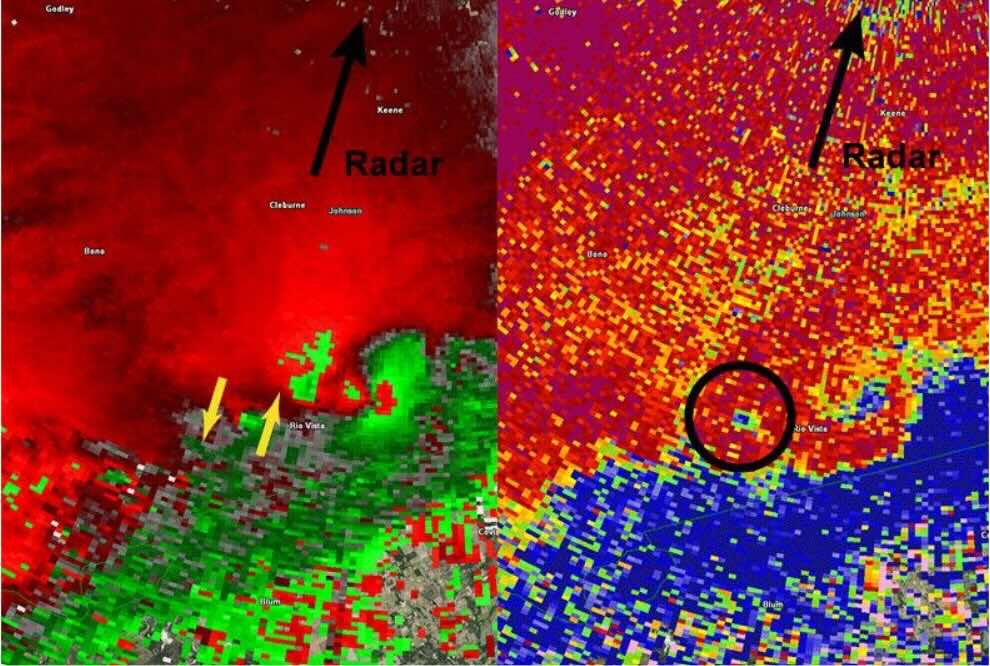

Source: Tony Hurt, National Weather Service
Why It Matters for Weather Enthusiasts
Understanding radar resolution gives you an edge in forecasting:
- Track storms more accurately. See distinct storm features instead of blurry blobs.
- Improve precipitation estimates. Avoid over- or underestimating rainfall intensity.
- Enhance severe weather awareness. Detect storm structures that indicate potential tornadoes or damaging winds.
Knowing which radar sources provide the best resolution can help you make smarter decisions and enjoy a more precise forecasting experience.
How to Optimize Your Radar Experience
1. Choose the Right Radar Source
Apps like Rain Viewer provide radar feeds from multiple sources, including high-resolution data when available. Look for:
- The highest resolution option.
- Fast update intervals for real-time tracking.
- Multi-source radar integration to fill gaps in coverage.
2. Adjust Your View
- Zoom in to analyze storm details.
- Zoom out to spot larger weather trends.
3. Pair Radar with Other Data
Radar is powerful, but combining it with satellite imagery, wind patterns, and temperature data provides a fuller picture of evolving weather.
Additionally, check historical radar loops to see how a storm has evolved over time. This can give clues about future movement and intensity trends.
Advanced Radar Features to Look For
If you want the best radar experience, keep an eye out for these advanced features:
- Dual-polarization radar. Provides better insights into precipitation types and intensity.
- Velocity scans. Show wind movement inside storms, crucial for spotting rotation.
- Composite reflectivity. Combines multiple radar levels to give a 3D view of storm structures.
- Radar-derived precipitation estimates. Help gauge actual rainfall amounts over time.
Final Thoughts
Radar resolution plays a critical role in how accurately you can track and predict weather. By understanding how spatial and temporal resolution impact radar imagery, you can make sharper forecasts and navigate storms like a pro.






